Bringing the WAN Edge into the Overlay
- In order to join the overlay network, a WAN Edge router needs to establish a secure connection to the vManage so that it can receive a configuration file, and it needs to establish a secure connection with the vSmart controller so that it can participate in the overlay network.
- The discovery of the vManage and vSmart happens automatically and is accomplished by first establishing a secure connection to the vBond orchestrator.
The
following figure shows the sequence of events that occurs when bringing the WAN
Edge router into the overlay.
- Through a minimal bootstrap configuration or through the automated provisioning (ZTP or PnP) process, the WAN Edge router first attempts to authenticate with the vBond orchestrator through an encrypted DTLS connection. Once authenticated, the vBond orchestrator sends the WAN Edge router the IP addresses of the vManage network management system (NMS) and the vSmart controllers. The vBond orchestrator also informs the vSmart controllers and vManage of the new WAN Edge router wanting to join the domain.
- The WAN Edge router begins establishing secure DTLS or TLS sessions with the vManage and the vSmart controllers and tears down the session with the vBond orchestrator. Once the WAN Edge router authenticates with the vManage NMS, the vManage pushes the configuration to the WAN Edge router if available.
- The WAN Edge router attempts to establish DTLS/TLS connections to the vSmart controllers over each transport link. When it authenticates to a vSmart controller, it establishes an OMP session and then learns the routes, including prefixes, TLOCs, and service routes, encryption keys, and policies.
- The WAN Edge router attempts to establish BFD sessions to remote TLOCs over each transport using IPsec.
Onboarding the
WAN Edge Router
There are multiple ways to get a WAN Edge router up and running on the network.
- One way is the manual method, where you can establish a console to the device and configure a few configuration lines, or
- By using an automated provisioning method, like Zero-Touch Provision (ZTP) or Plug-and-Play (PnP), where you can plug the WAN Edge router into the network and power it on and it will be provisioned automatically.
Manual
With the
manual configuration method, the idea is to configure the minimum network
connectivity and the minimum identifying information along with the vBond
orchestrator IP address or hostname.
The WAN Edge router attempts to connect to
the vBond orchestrator and discover the other network controllers from there.
In order for you to bring up the WAN Edge router successfully, there are a few
things that need to be configured on the WAN Edge router:
- Configure an IP address and gateway address on an interface connected to the transport network, or alternatively, configure Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) in order to obtain an IP address and gateway address dynamically. The WAN Edge should be able to reach the vBond through the network.
- Configure the vBond IP address or hostname. If you configure a hostname, the WAN Edge router needs to be able to resolve it. You do this by configuring a valid DNS server address or static hostname IP address mapping under VPN 0.
- Configure the organization name, system IP address, and site ID. Optionally, configure the host name.
Automated
Device Provisioning (ZTP or PnP)
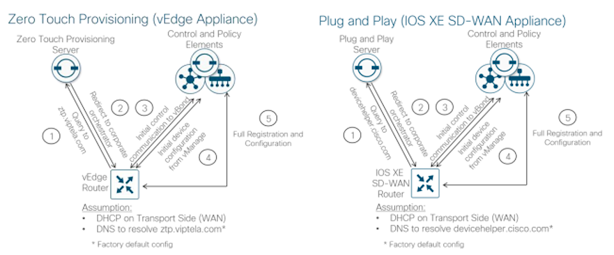
- Automated device provisioning for vEdge devices is called Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP), and for IOS XE SD[1]WAN devices, it is called Plug-and-Play (PnP).
- The processes are very similar, but two different services are involved.
- The automated provisioning procedure starts when the WAN Edge router is powered up for the first time.
- The vEdge router attempts to connect to a ZTP server with the hostname ztp.viptela.com, where it gets its vBond orchestrator information.
- For IOS XE SD-WAN routers, it attempts to connect to the PnP server using the hostname devicehelper.cisco.com.
- Once the vBond orchestrator information is obtained, it can then subsequently make connections to the vManage and vSmart controllers in order to get its full configuration and join the overlay network.
There are a
few requirements for automated device provisioning:
- With the hardware vEdge appliances, only certain ports are pre-configured by default to be a DHCP client interface and can be used for ZTP. The following table outlines the ports that must be plugged into the network for ZTP to work. With IOS XE SD-WAN devices, PnP is supported on all routed Gigabit Ethernet interfaces with the exception of the management interface (GigabitEthernet0).
- The WAN Edge router should be able to get an IP address through DHCP or use Auto IP (vEdge only) to discover an IP address.
- The gateway router for the WAN Edge router in the network should have reachability to public DNS servers and be able to reach ztp.viptela.com for vEdge devices and devicehelper.cisco.com for IOS XE SD-WAN devices. A ZTP server can be deployed on-premise but the PnP server requires Internet access.
- The SD-WAN device needs to be correctly entered in the PnP portal at https://software.cisco.com and associated with a controller profile defining the vBond hostname or IP address information.
- In vManage, there must be a device configuration template for the WAN Edge router attached to the WAN Edge device. The system IP and site ID need to be included in this device template in order for the process to work. The ZTP or PnP process cannot succeed without this.


No comments:
Post a Comment