Traditional IT Overview
How do websites work?
- Well, we have a server hosted somewhere, and we, as a web browser, and want to get access to that server to visualize a website.
- What we are going to do as a client is use a network.
- A network between us and the server, and the client will find the network and will use network to route the packets, the data into the server, then the server will reply to us, and we will get the response, and we can view a website.
- Obviously, that is very simplified, but that gives you an idea.
- Now for the clients to find the server and the server to find the clients, you need to have IP addresses. So, a clients have IP addresses and a server also have an IP address.
- And so, the idea is that when you use an IP address, you can send a request to wherever you want to the server you want, and the server can know how to find you back.
- This is very similar to when you are writing some letters to your friend.
- For example, you would write a letter, and that would be your data, and you would be the client, then when you send the letter you put it in your mailbox, and then the network will be the network of the post office, then the post office will use network and the address you put on the letter to route your letter to the destination, which is, in this case, the server, and then if your correspondent wants to reply you back, they can use the address you put on the back of the envelope to write you back, and again, use the same network to get the letter back to you.
- So, servers are just like the network of your mail.
- Hopefully that's a good analogy.
- Well, a server is going to contain a CPU, and a CPU is a little piece that will be doing some computations, it will be very helpful to do some calculations and find results, and then, your server also needs RAM, or memory. This is going to be very, very fast memory, which will allow us to store information and retrieve it very quickly.
- Now we also need to have some more long-term storage of data.
- Obviously, it's still in our brain as humans, but in computers, we have included some special storage to store data, for example, files, and then if we want to store the data in a more structured way, we're going to use a database, and a database is going to be data formatted in a way that we can easily search it and query it.
- Finally in the server, we're also going to have some networking aspect. So, there's going to be the routers, switch, DNS servers.
- All these things are going to super important going forward because the cloud is going to be giving these things for us on demand.
IT Terminology
- Network: cables, routers and servers connected with each other
- Router: A networking device that forwards data packets between computers networks. They know where to send your packets on the internet!
- Switch: Takes a packet and send it to the correct server / client on your network
So, if we put all these things together. Our client will send the data to a router, the router will find its way all the way to a switch, and the switch will know to which computer in your network to send the data to.
So why do I introduce all these things?
Well, let's go back to traditional IT.
- When people used to start websites or companies before, they used to do it in their home or their garage, and so they would literally go to the store, buy a server, and they put the server in their home.
- You know, Google was started in a garage.
- Now, as your website grows, you need to add more and more servers to serve that demand, and so your home starts to be filled with servers. So, this bad right, but your company is getting bigger, you're generating some money so you're going to move to your own office, and you decide to allocate a special room which is going to be called a data centre.
- In a data centre, you're going to have, again, your servers, and you're going to be able to scale them by adding and purchasing more and more servers.
- Now this worked, and this worked for so many years, but there are a few problems with this approach.
Problems with traditional IT approach
- Pay for the rent for the data centre
- Pay for power supply, cooling, maintenance
- Adding and replacing hardware takes time
- Scaling is limited
- Hire 24/7 team to monitor the infrastructure
- How to deal with disasters? (Earthquake, power shutdown, fire…)
And the answer is yes, and that will be the cloud.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power,
database storage, applications, and other IT resources.
- The very important keyword here is on-demand, you get it when you need it.
- And then through a cloud service platform, you're going to get a pay-as-you-go pricing.
- That means that you're only going to pay for what you requested when you requested it and as you're using it, when you're done using it, you're not going to pay anymore.
- So, in cloud computing we can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need.
- Do you need a big server? We have that for you.
- Do you want a small one? We have that too.
- Do you want 10? Yes.
- Do you want two tomorrow? Of course.
- Then you can access all these resources, not with 24-hour notice, not with two hours’ notice, but instantly, you don't need to order things in advance.
- Then the cloud will also give you a really nice interface so, you can easily access your servers, your storage, databases, and a set of application services.
Some Cloud services which we already using
Deployment Models of the Cloud
Private Cloud
- The provider could be Rackspace.
- This is cloud services used by a single organization, they're not exposed to the public, so, you get your own private cloud, your own private data center, it's just managed by someone else.
- You still have complete control over it, and you have more security for a sensitive application, which may need some specific business needs.
Public Cloud
- Three famous cloud providers are Microsoft Azure, Google cloud, and Amazon Web services.
- The cloud resources own and operated by a third-party cloud service provider, and they're delivered over the Internet.
Hybrid Cloud
- With hybrid, we're actually getting the mix of private and public.
- We're going to keep some servers on premises, and we'll extend some of the capabilities we need into the cloud. That means that we'll have a hybrid of our own infrastructure and the AWS cloud.
- We'll have control over sensitive assets in your private infrastructure, but we'll have the flexibility and the cost effectiveness of using the public cloud.
Five Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand self-service:
- Users can provision resources and use them without human interaction from the service provider
- Broad network access:
- Resources available over the network, and can be accessed by diverse client platforms
- Multi-tenancy and resource pooling:
- Multiple customers can share the same infrastructure and applications with security and privacy
- Multiple customers are serviced from the same physical resources
- Rapid elasticity and scalability:
- Automatically and quickly acquire and dispose resources when needed
- Quickly and easily scale based on demand
- Measured service:
- Usage is measured, users pay correctly for what they have used
Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Trade capital expense (CAPEX) for operational expense (OPEX)
- Pay On-Demand: don’t own hardware
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Operational Expense (OPEX)
- Benefit from massive economies of scale
- Prices are reduced as AWS is more efficient due to large scale
- Stop guessing capacity
- Scale based on actual measured usage for our application
- Increase speed and agility
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers
- Go global in minutes: leverage the AWS global infrastructure
Problems solved by the Cloud
- Flexibility: change resource types when needed
- Cost-Effectiveness: pay as you go, for what you use
- Scalability: accommodate larger loads by making hardware stronger or adding additional nodes
- Elasticity: ability to scale out and scale-in when needed
- High-availability and fault-tolerance: build across data centers
- Agility: rapidly develop, test and launch software applications
Types of Cloud Computing
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provides networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Easy parallel with traditional on-premises IT
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Removes the need for your organization to manage the underlying infrastructure
- Focus on the deployment and management of your applications
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
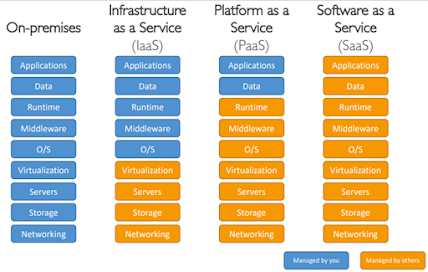
- On-premises is you're going to manage everything. So, your applications, your data, your runtime, your middleware, the operating system, virtualization, servers, storage, and networking.
- With IaaS, Infrastructure as a Service, we're going to manage the application, the data, the runtime, the middleware, and the OS, but all the virtualization, servers, storage, and networking, are going to be managed by others like AWS.
- With Platform as a Service, we manage even less. So, everything from the runtime to the networking is managed by AWS. And the only thing we care about when we use a Platform as a Service is our application and our data.
- And finally, well if you're using Software as a Service, everything is going to be managed by AWS.
Example of Cloud Computing
Types
- Infrastructure as a Service:
- Amazon EC2 (on AWS)
- GCP, Azure, Rackspace, Digital Ocean, Linode
- Platform as a Service:
- Elastic Beanstalk (on AWS)
- Heroku, Google App Engine (GCP), Windows Azure (Microsoft)
- Software as a Service:
- Many AWS services (ex: Rekognition for Machine Learning)
- Google Apps (Gmail), Dropbox, Zoom
Pricing of the Cloud – Quick Overview
AWS has 3 pricing fundamentals, following the pay-as-you-go
pricing model
- Compute:
- Pay for compute time
- Storage:
- Pay for data stored in the Cloud
- Data transfer OUT of the Cloud:
- And for the networking, we're going to only pay when the data leaves the cloud.
- Data transfer IN is free. Any data that goes into the cloud is free
And this solves the expensive issue of traditional IT.



No comments:
Post a Comment